Polarisation
des Nachthimmels am Paranal

The
Olbers paradox shows the resulting contradiction in the prediction of a
bright night sky and its actual dark appearance. Heinrich Wilhelm
Olbers formulated this problem in 1823. It concerns world models that
correspond to the perfect cosmological principle. In an infinitely
extended universe with a uniform distribution of stars over long
distances. Under these conditions, the light of a star would have
reached the earth from every direction and the sky would appear at
least as bright as the surface of the stars after a long time.
The problem resolved itself as mam realized that the universe is
unlimited but not infinite and expands.

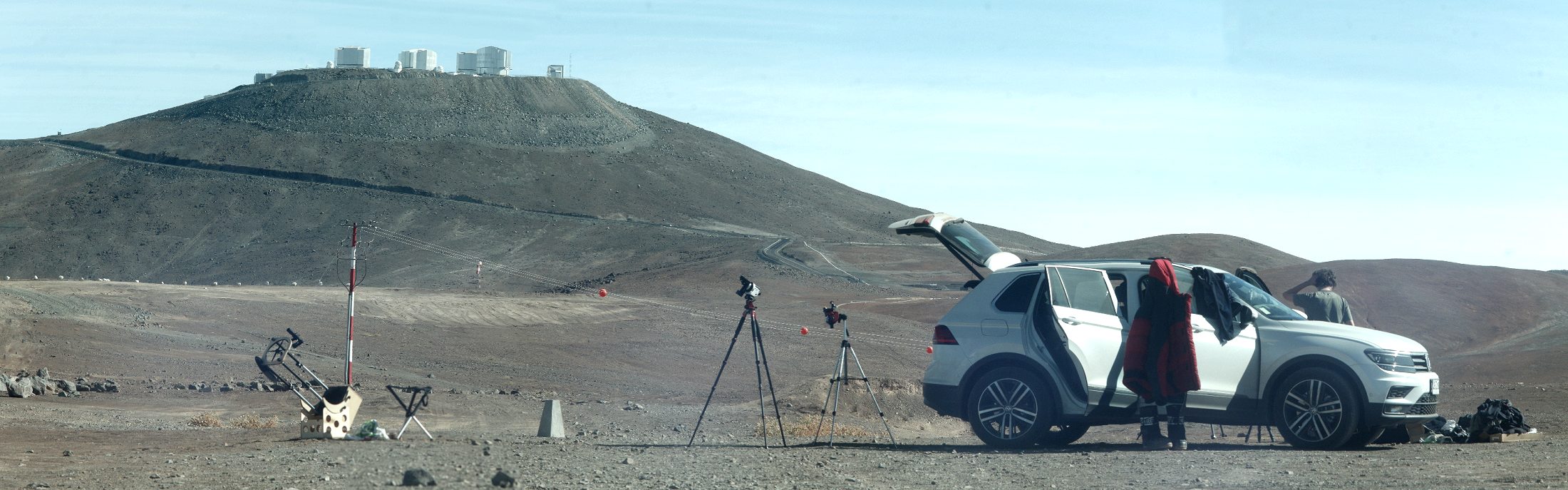
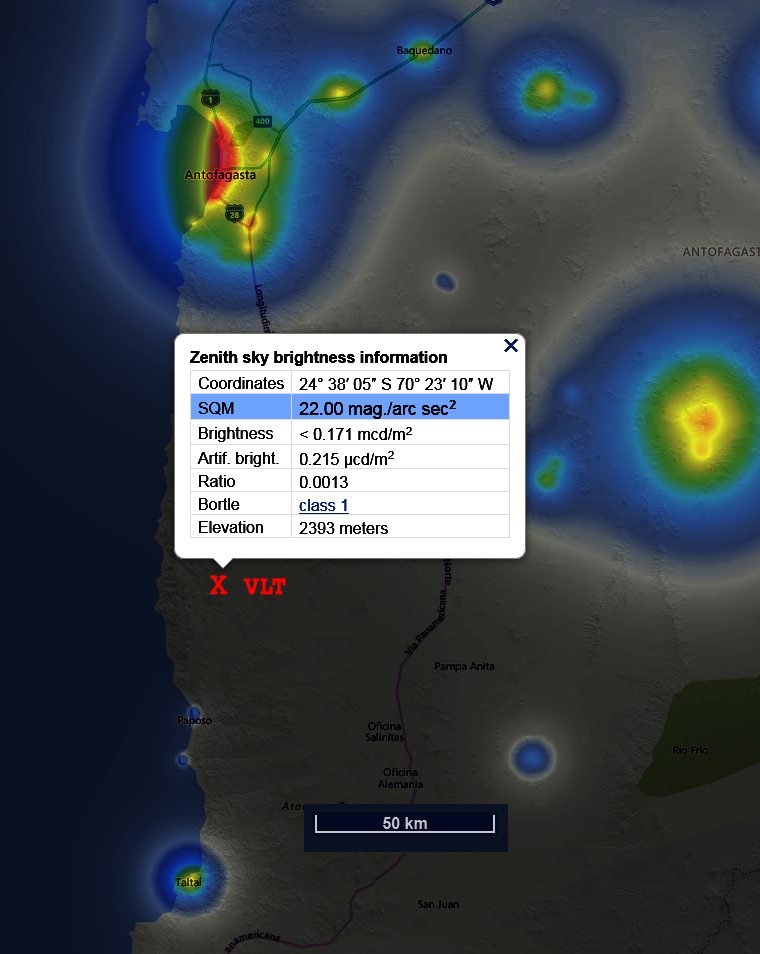
The Paranal considered one of the darkest
locations in the world -
even here the is
night sky isn´t not, between the stars is still one
To recognize sky lights.


Night-Sky-Videos
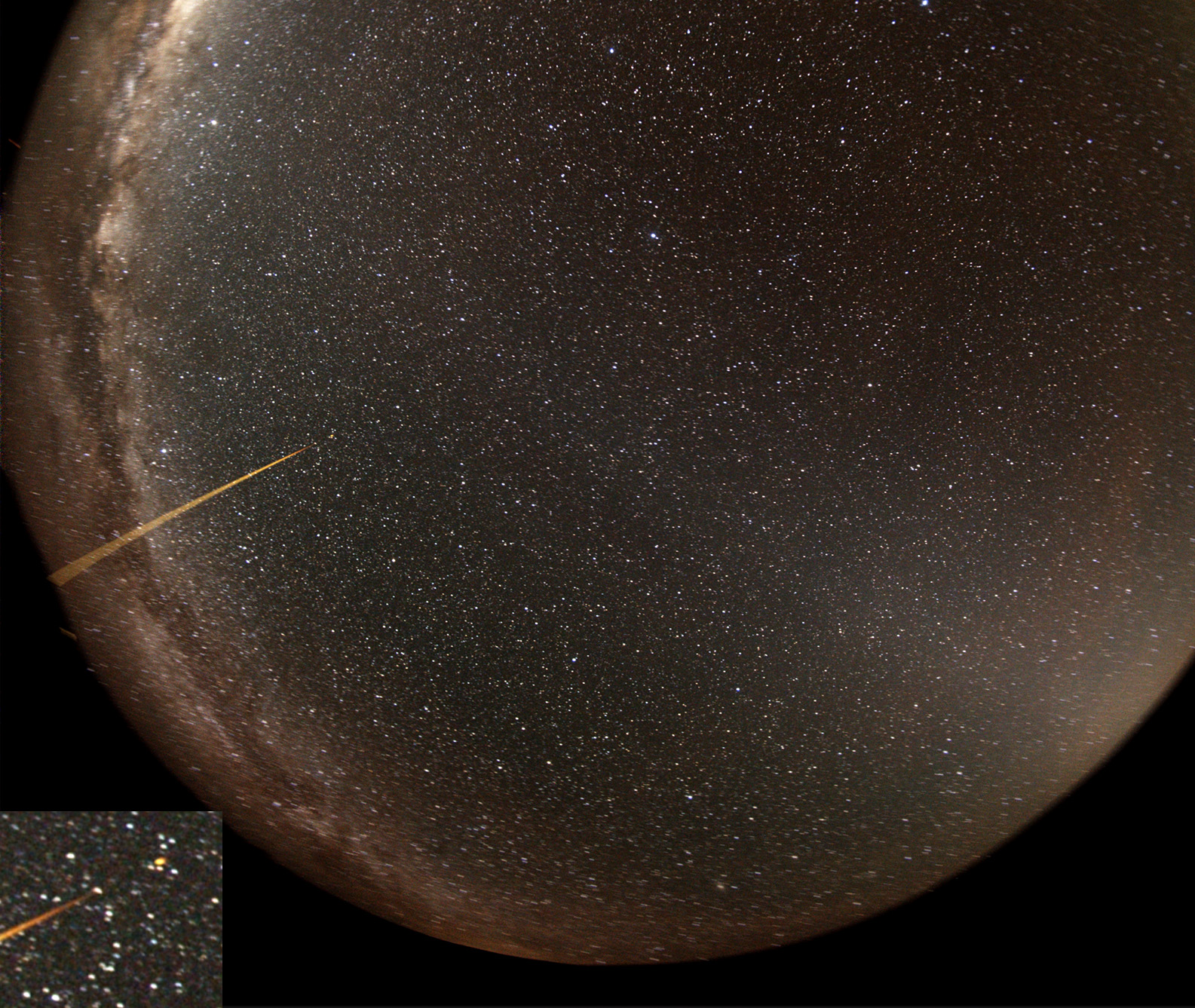

Why is the sky not really dark?
3 possible solutions:
-light comes from outside the solar System (Galactic cirrus)
-light comes from inside the solar system (Zodiacal light)
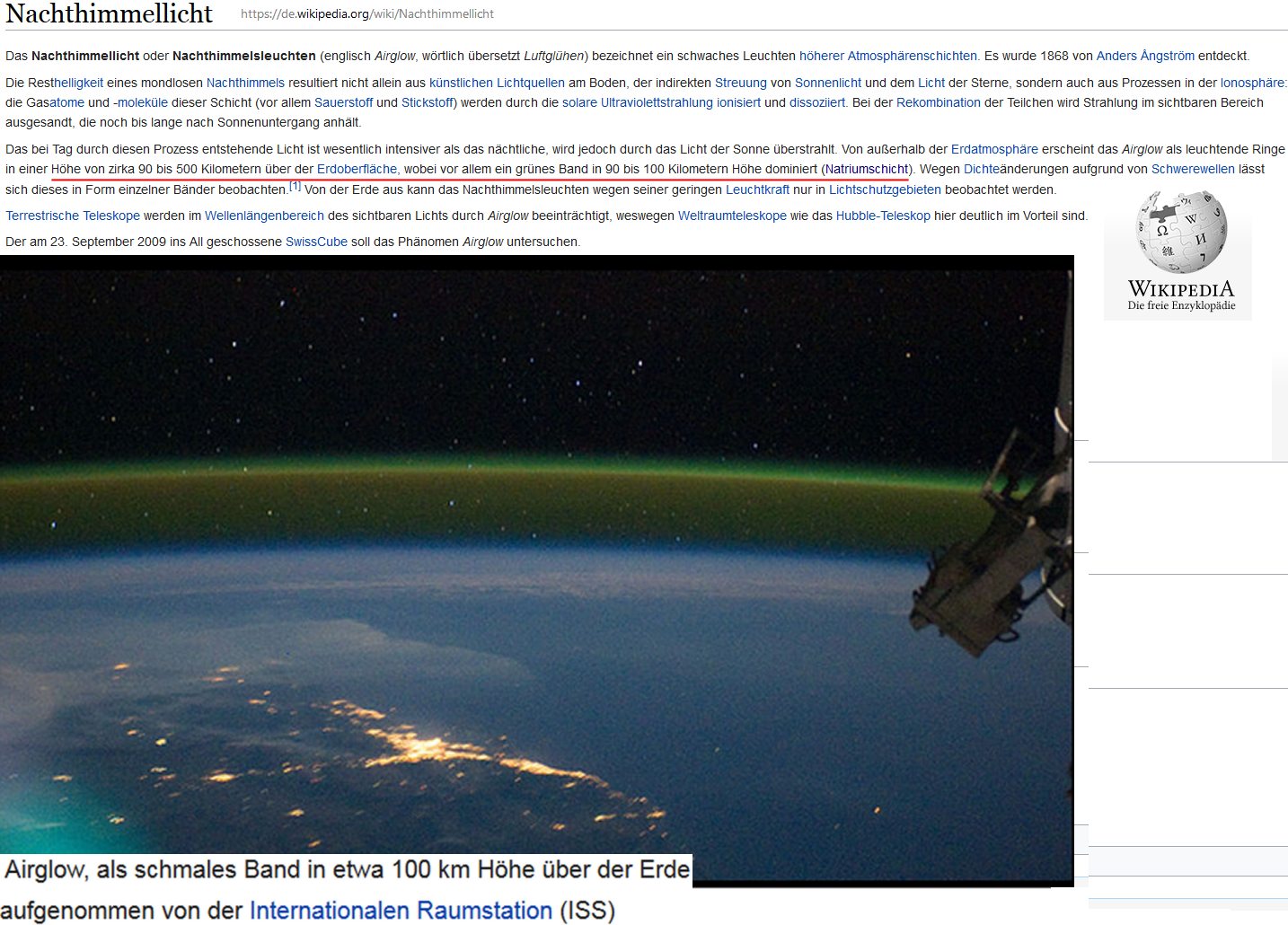
-light comes from earth (Airglow: recombination-effects in the upper
atmosphere)
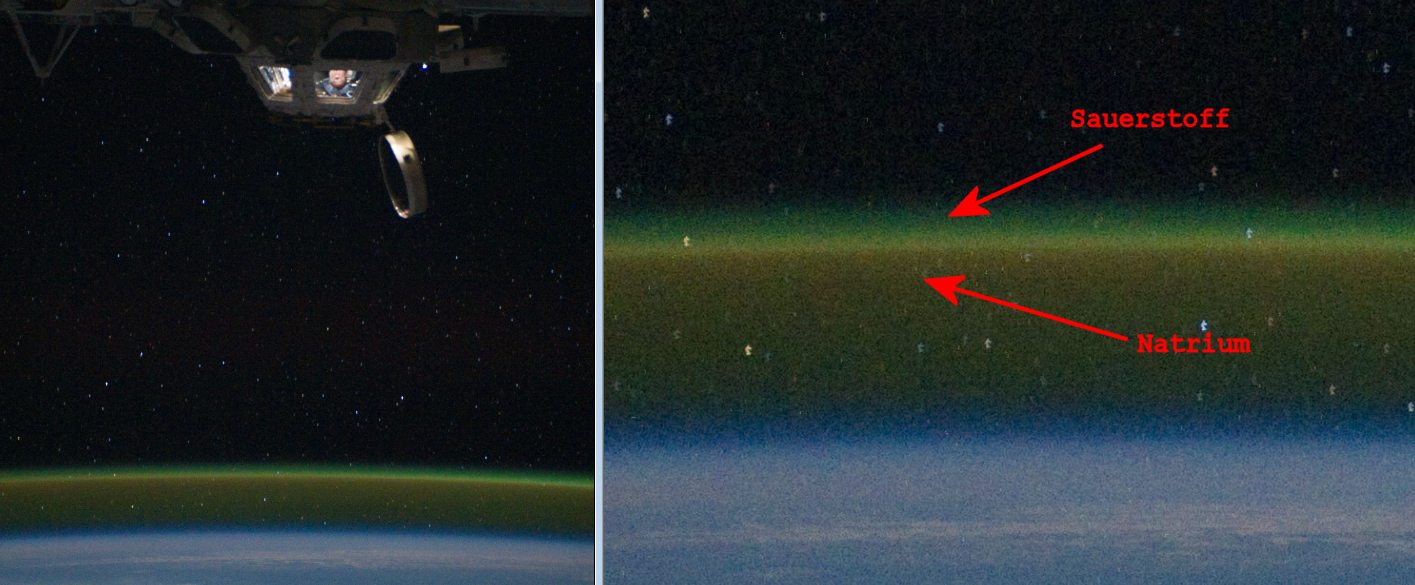
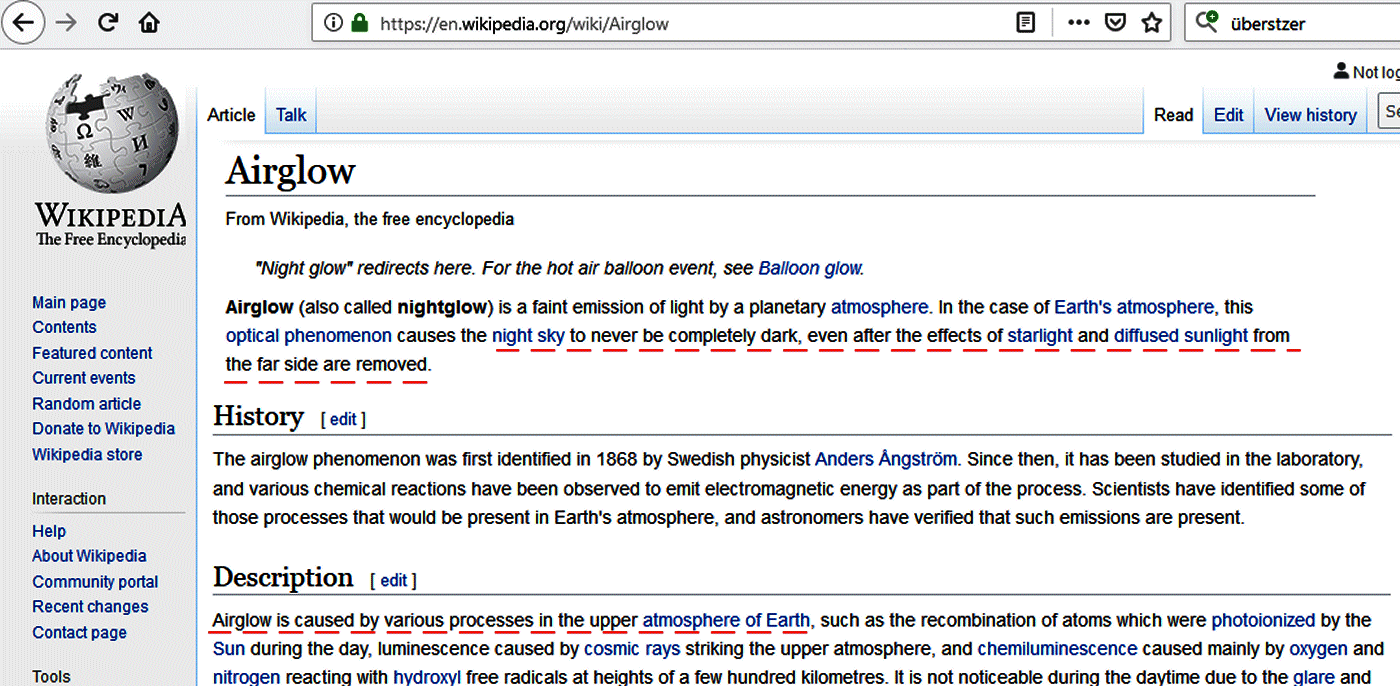
The airglow phenomenon has various chemical reactions which have been
observed to emit electromagnetic energy as part of the process.
Domestic are:
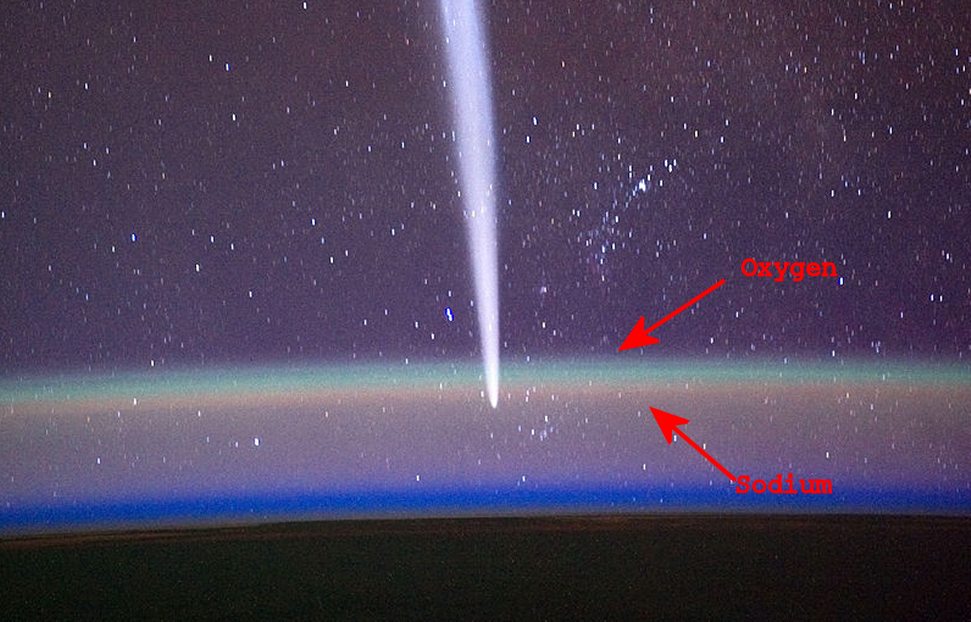
- the green one: 90 - 100 km by Oxigen
- the red one: <90 km red-yellow by Sodium (Na)
Well visible is the airglow from the ISS:


Galactic Cirrus:
(Integrated Flux Nebula)
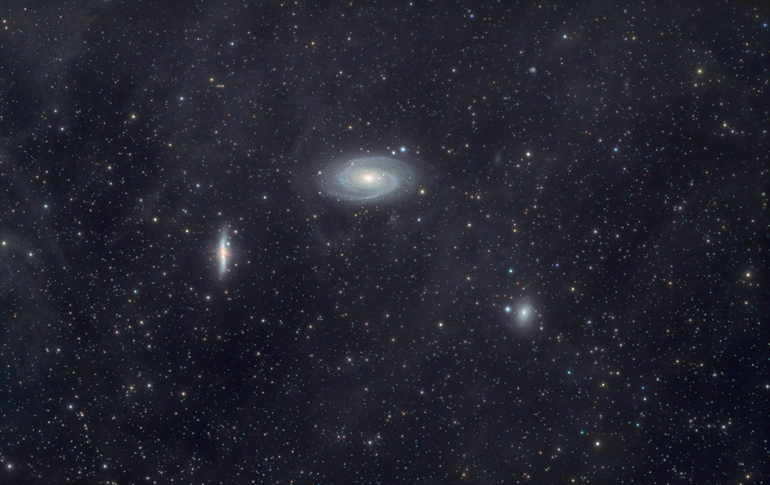
M 81/82 with a long exposure time:

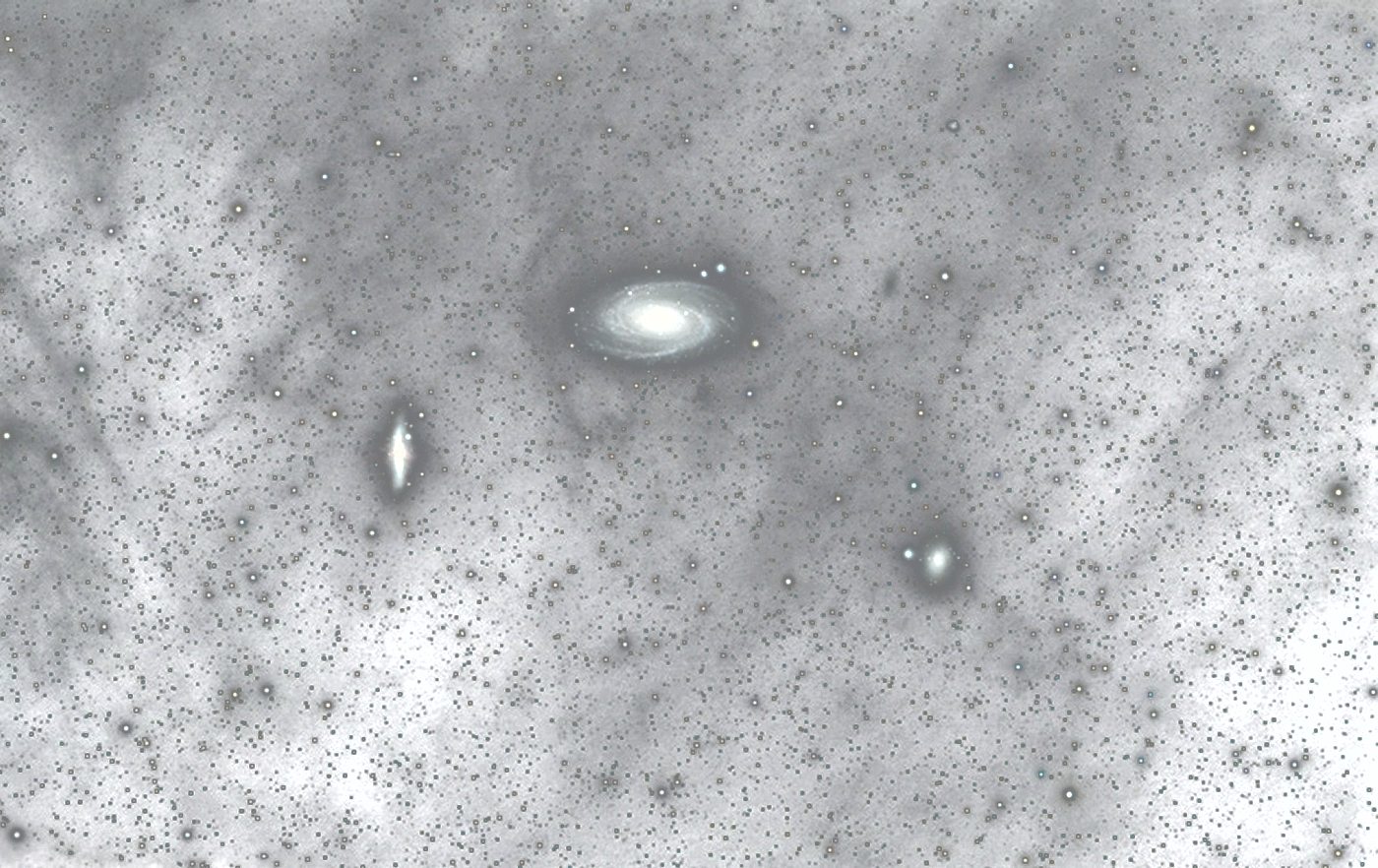
Galactic dust ist best
visble in Infrared, but its also visible as reflection nebular at very
lon Exposure times.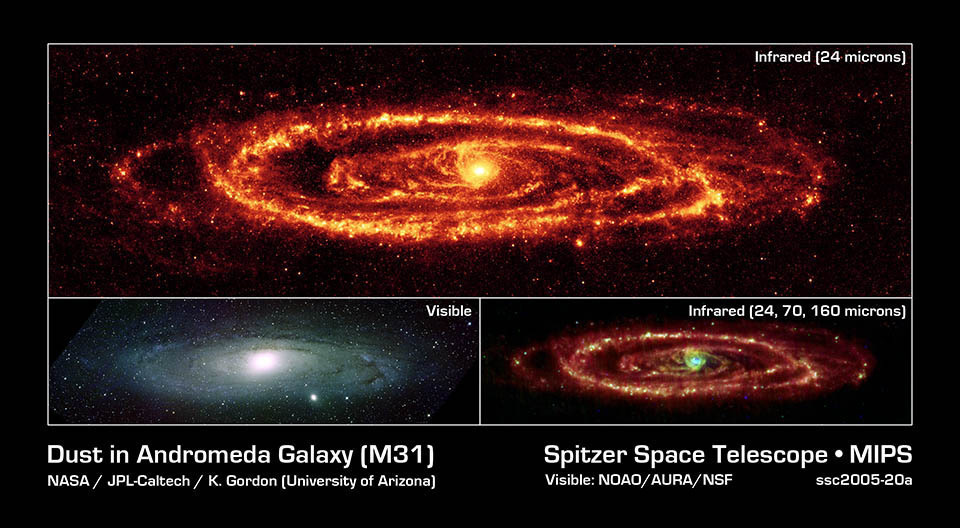

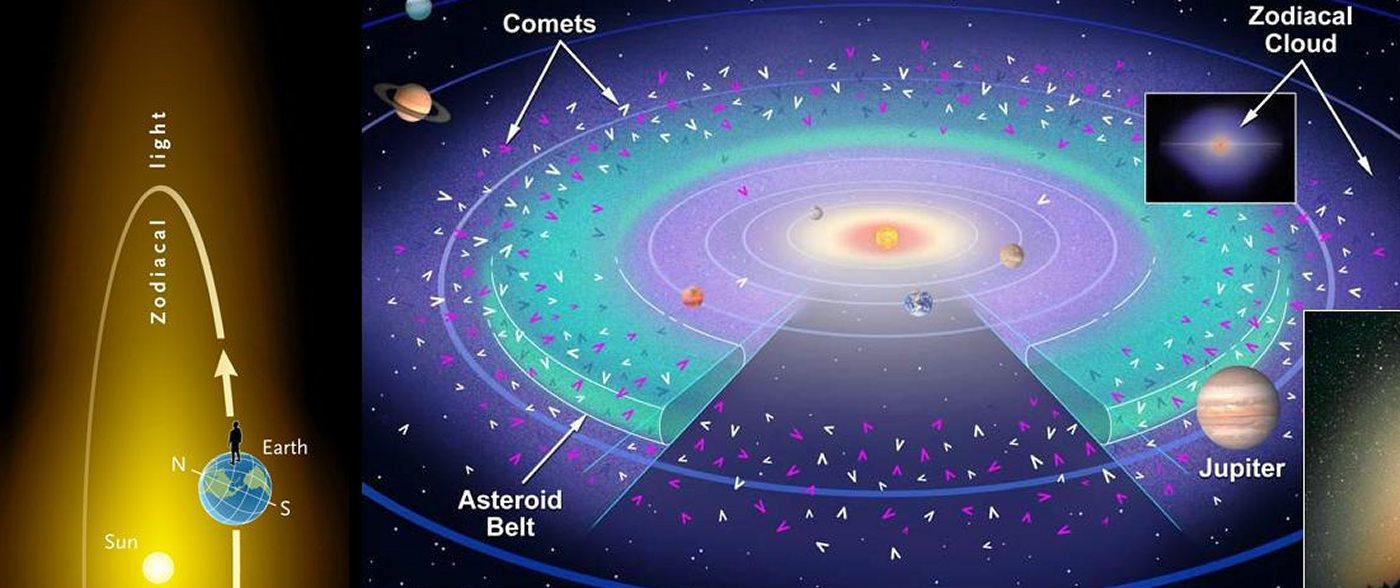
Jupiter produces structures in
the Zodical Light which we were able to photograph in Chile with long
exposure times.
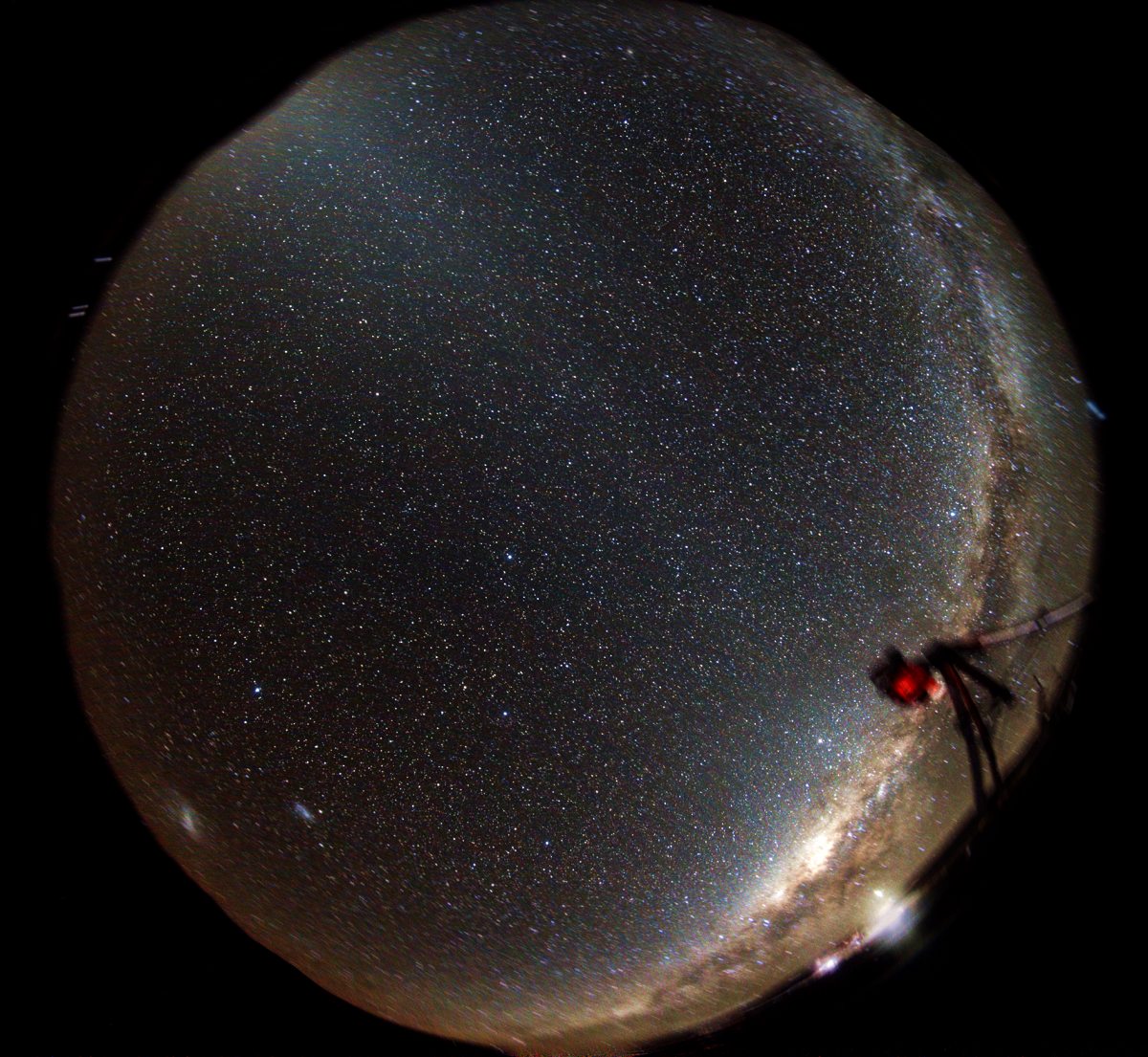

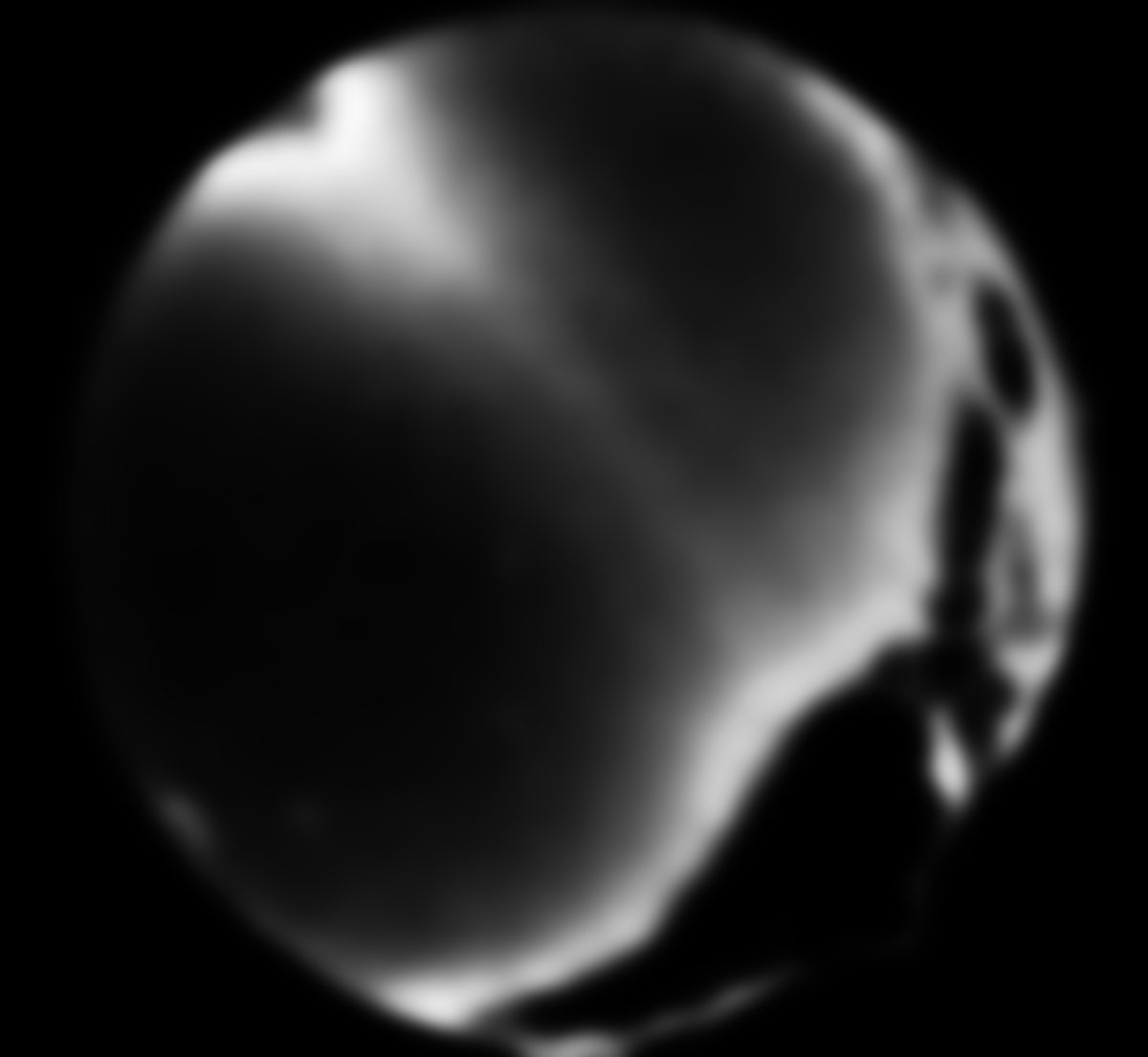

But the question ist: What´s the light outside the zodical
band and the band of the Milky way?
Depends ist on the Galaxy or on the solar system or on the earth??

Possible solution to find an answer:
Galactic
Cirrus and Zodiacal
light are reflections
on dust an should
be polarized.
---> If the Night-Glow depends on Galactic Cirrus, the
polarization
should change with the position of the Milky Way.
---> If the Night-Glow
depends on Zodiacal
light,
the
polarization should
change with the position of the sun
---> If
the Night-Glow
depends on light
comes from earth (Airglow), the
polarization should be independend during
the night
Die
Polarisation des Zodiakallichtes war bei einem ersten Versuch 2018 in
Namibia unerwartet
stark. Ein geübter Beobachter konnte den
Effekt mit freien Auge sehen, wenn er den Filter vor dem Auge
drehte.
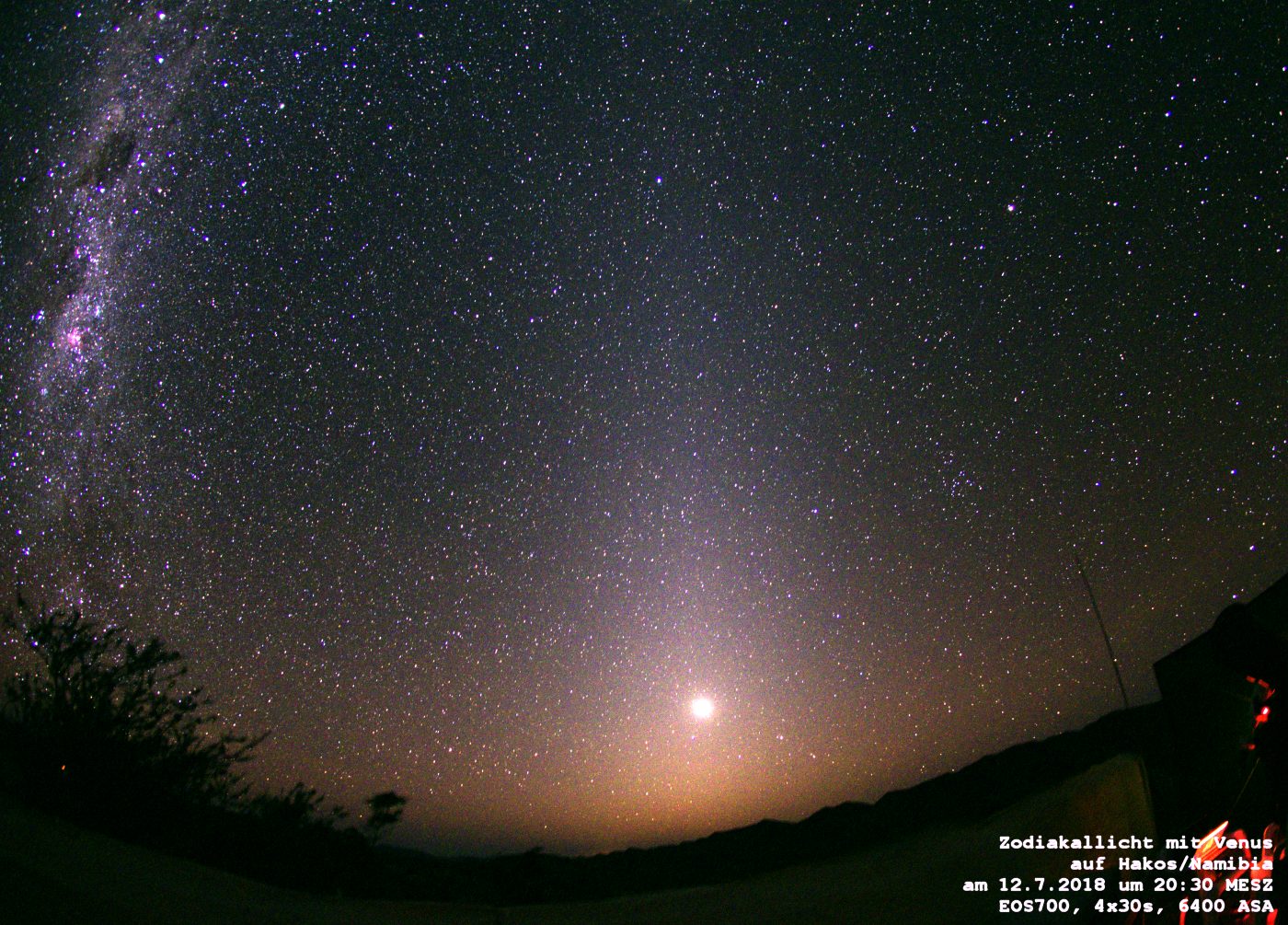

Mit
der Software Iris wurde ein Polarisationsgrad von etwa
30% gemessen.

Auswertung mit IRIS


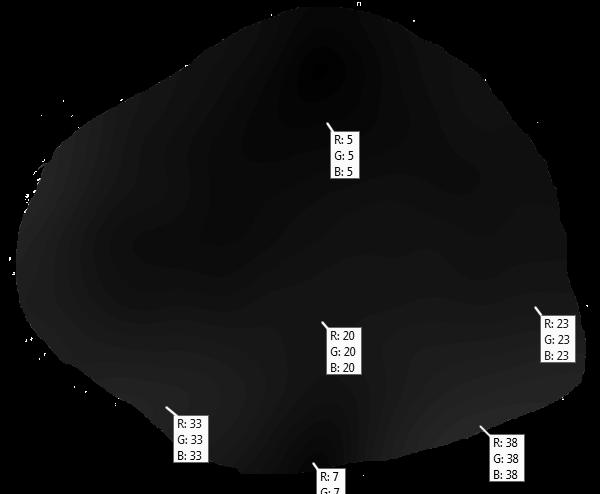

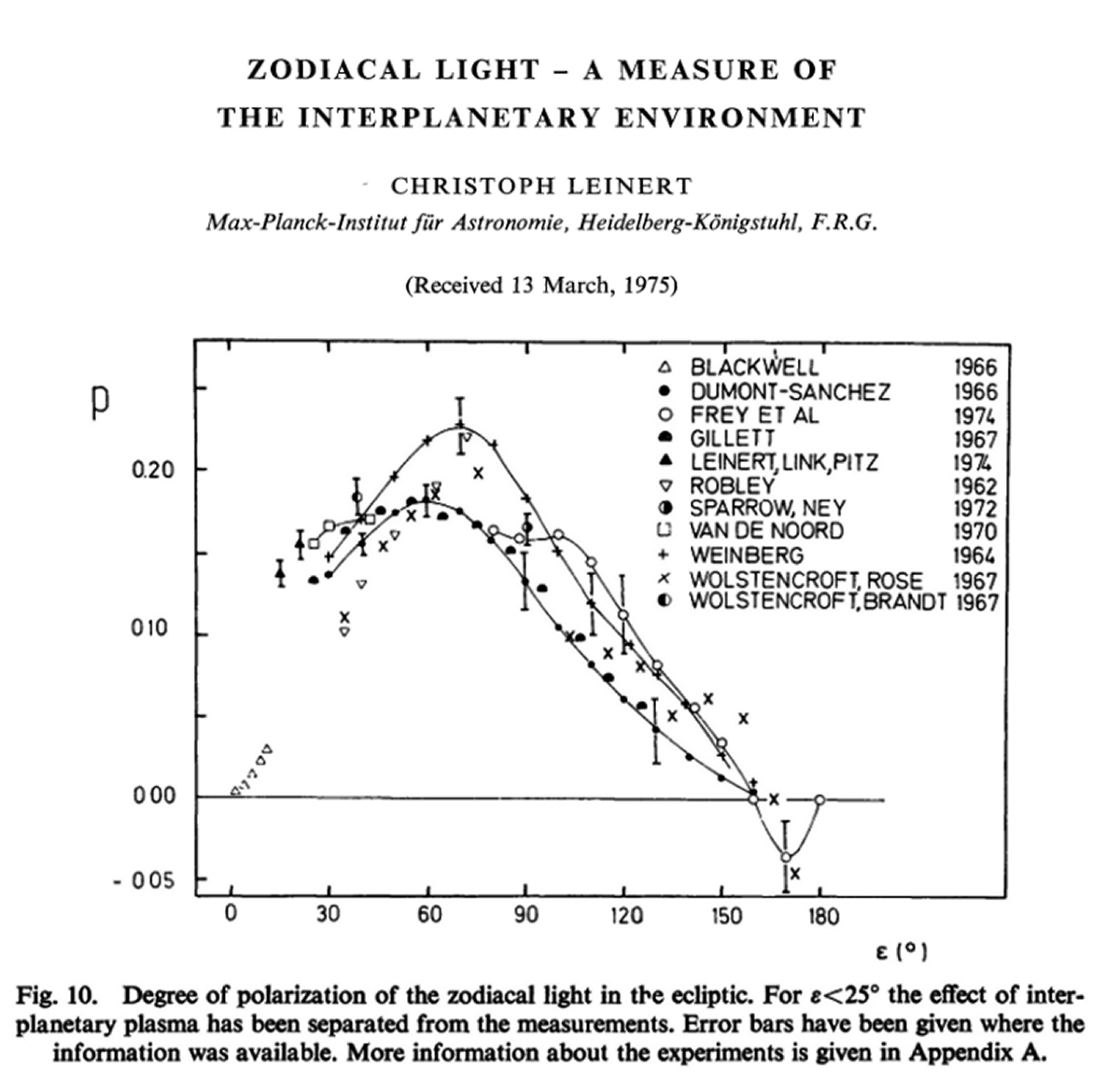
Die gemessenen 20% bei 60 Grad Elogation decken sich gut mit Angaben
aus der Fachlitertur.
Etwas
unklar blieb, ob die Polarisation tatsächlich
aus dem
Zodiakallicht kommt oder ein überlagernder Effekt des
polarisierten Nachthimmels ist.
Daher
wurde am Morgen nochmal der Himmel als ganzes auf Polarisation
unterssucht. Der Effekt ist erstaunlich.
Polarisation
des Gesamthimmels
als Animard Gif


Für die Polarisation des Gesamthimmels sind verschiedene
Ursachen denkbar. Ein kumulierter Effekt des Galaktischen Zirrus, ein
Leuchten in unserer Erdatmosphäre oder Reflektion
des Sonnenlichts am planetaren Staub abseits des
Zodiakallichtes. Das es auch außerhalb der Ekliptik Staub
geben muss, ist bekannt. Schließlich laufen dort auch Kometen
auf polnahen Bahnen. Wenn die Polarisation durch die Sonnen verursacht
wird, sollten die Polarisationswinkel einen Bezug zu Sonne haben. Das
läßt sich gut durch eine Überlagerung mit
einem Planetariumsprogramm beweisen.
Zunächst
wurde untersucht welcher Abschnitt des Himmels überhaupt
fotografiert wurde. Der Filter führte doch zu einer recht
starken Abschattung und das Feld ist relativ klein.
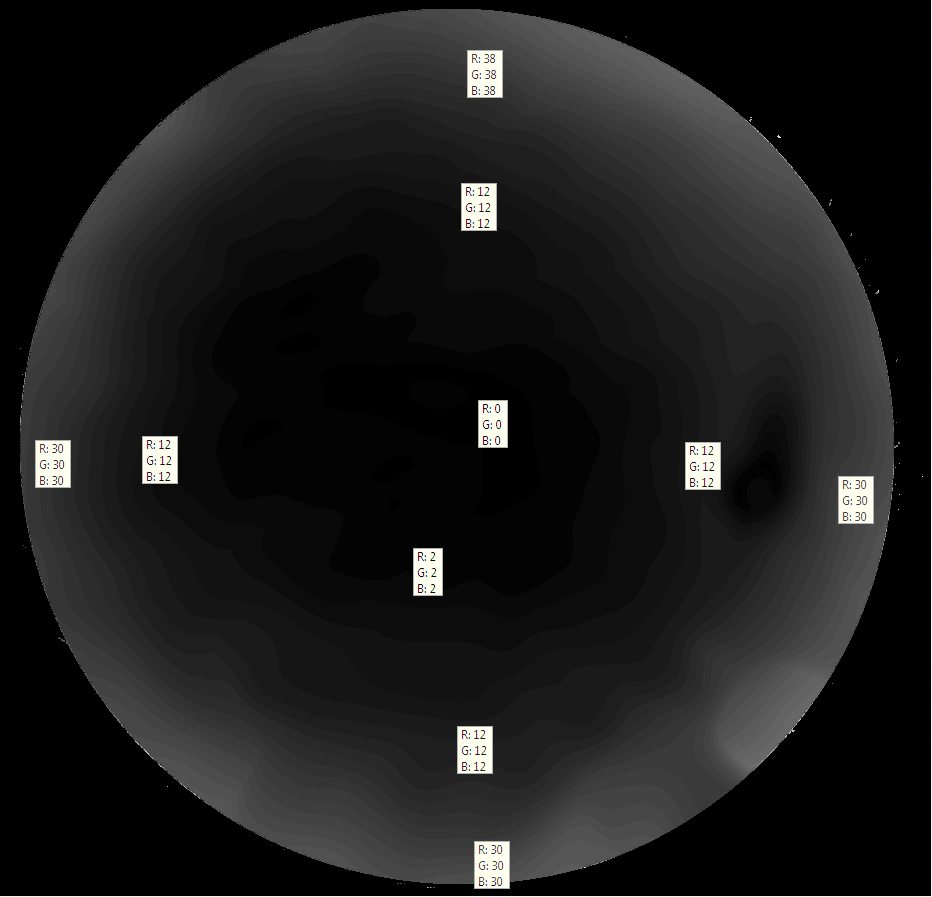
Dann
wurden die Polarisationsgrade im Feld gemessen und die
Polarisationswinkel
bestimmt.
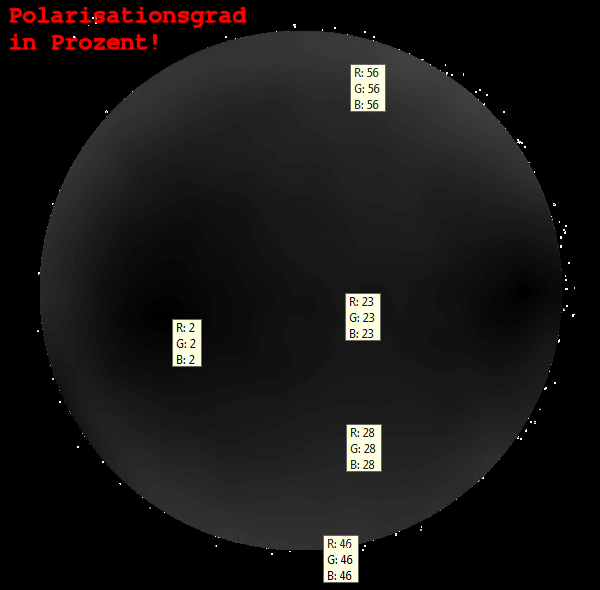

Abschließend
wurde alles wieder
per
Animation im Bezug zur Sonne gesetzt
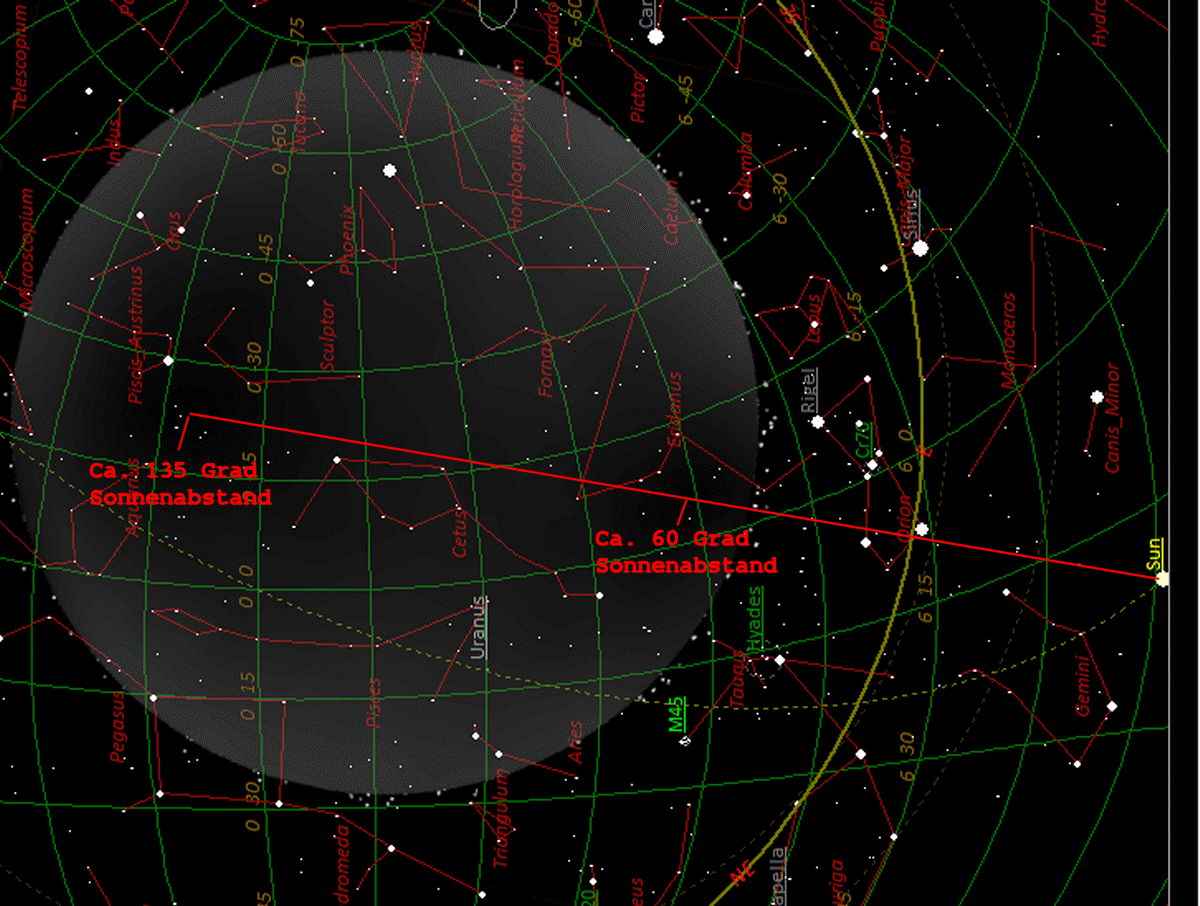
Der Bezug zur Sonne ist eindeutig. Die
Minima liegen auf einer Linie mit einem Sonnenabstand von etwa 60 und
135 Grad.
Unklar ist noch wie das Resultat interpretiert werden muss.
Is
it a coincidence
?
Wikipedia says:
2.
Chance:
Chile 2019
Diesmal wurde mit einem Fisheye und einem geößeren
Filter gearbeitet:
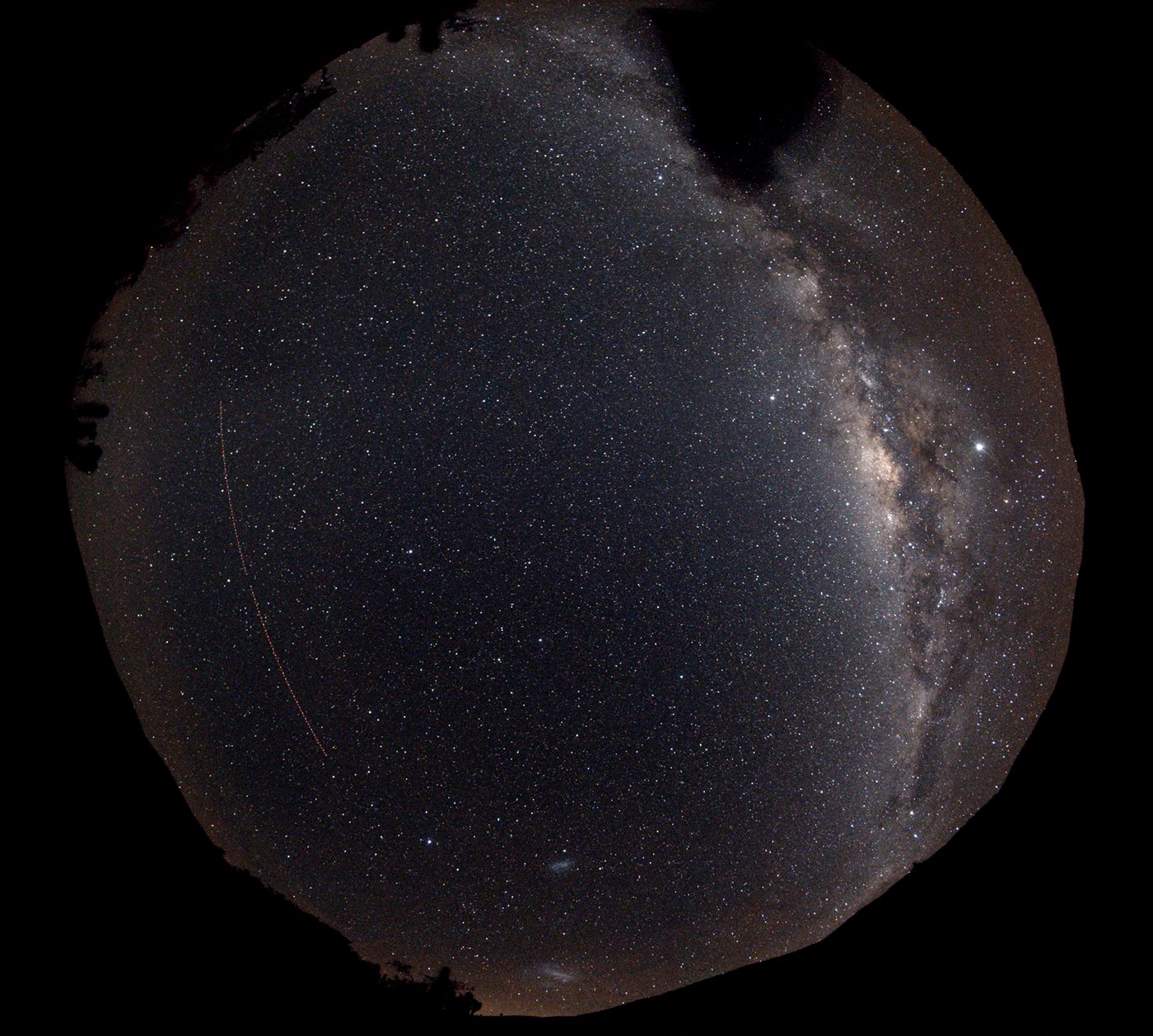



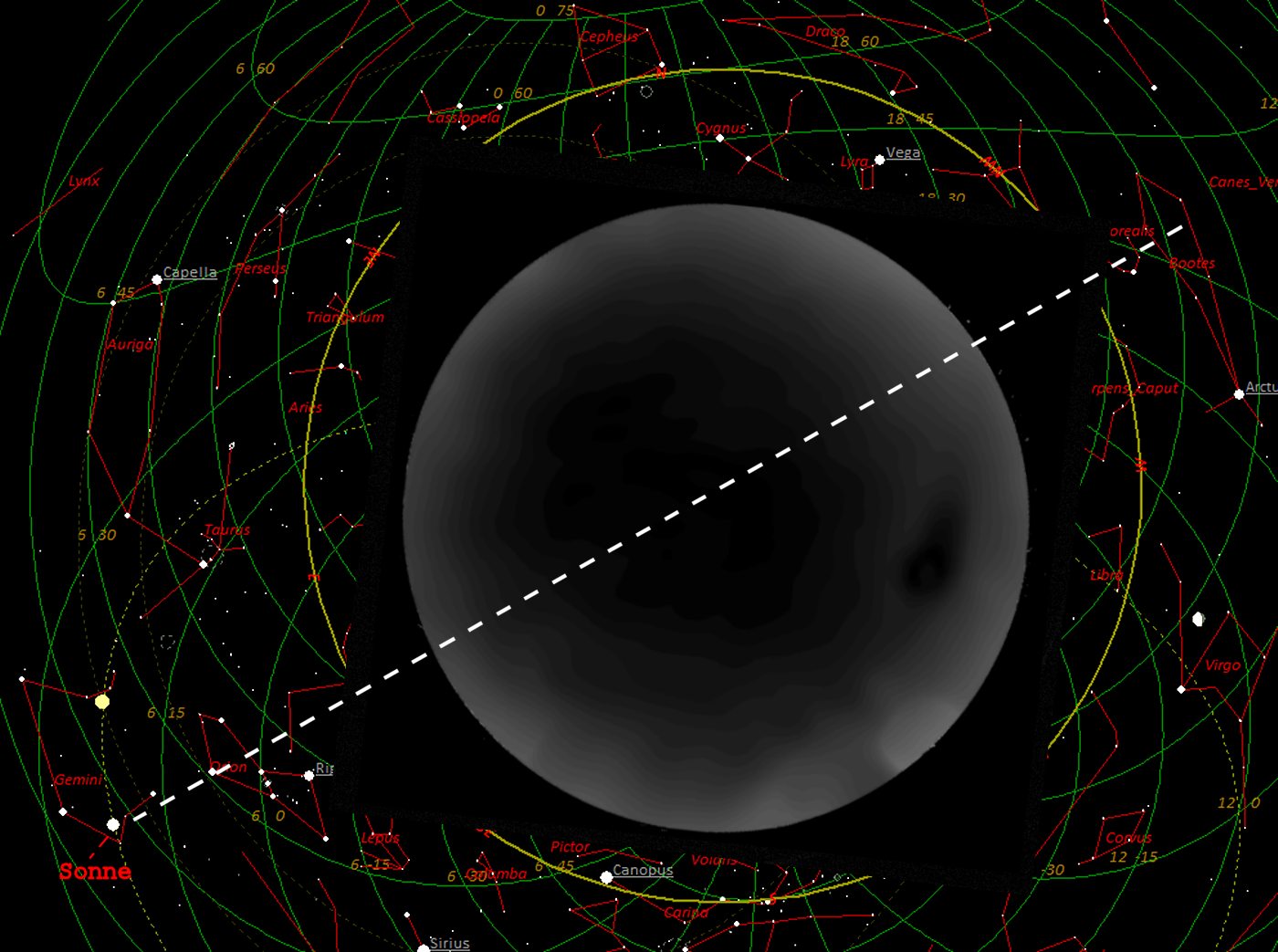
---->
No relation between polarization of the night sky an the position of
the sun!
(open question: But perhaps an influence
oft the Milky way?)
Second
measurement
without Milky Way:
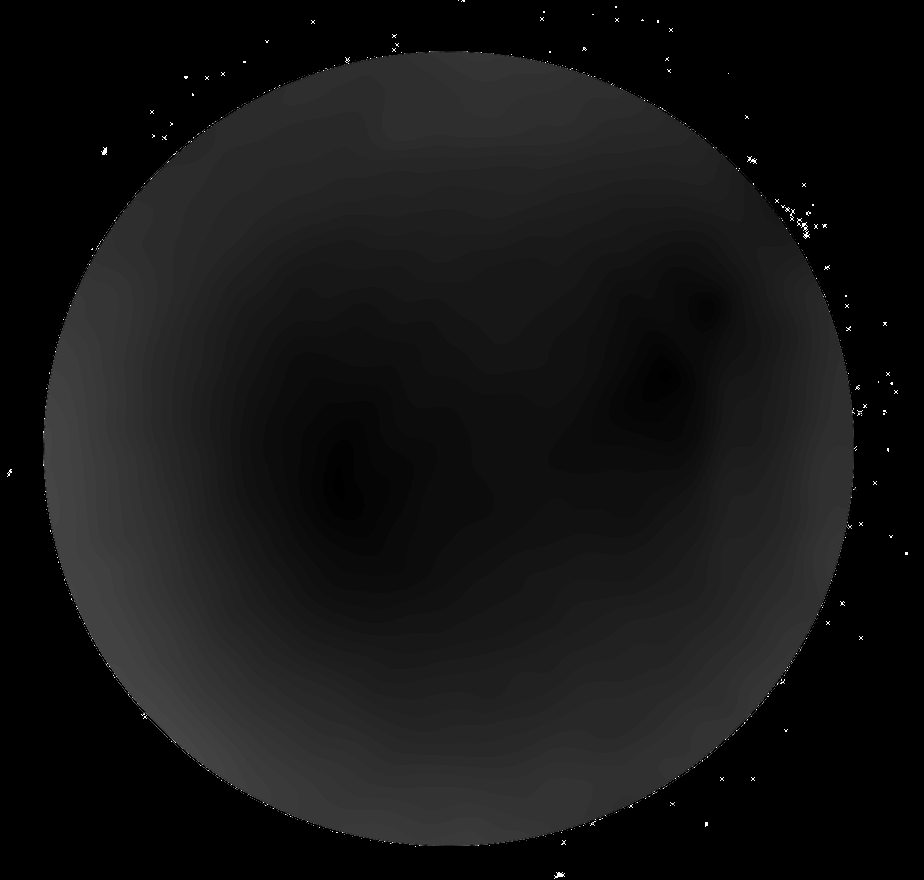


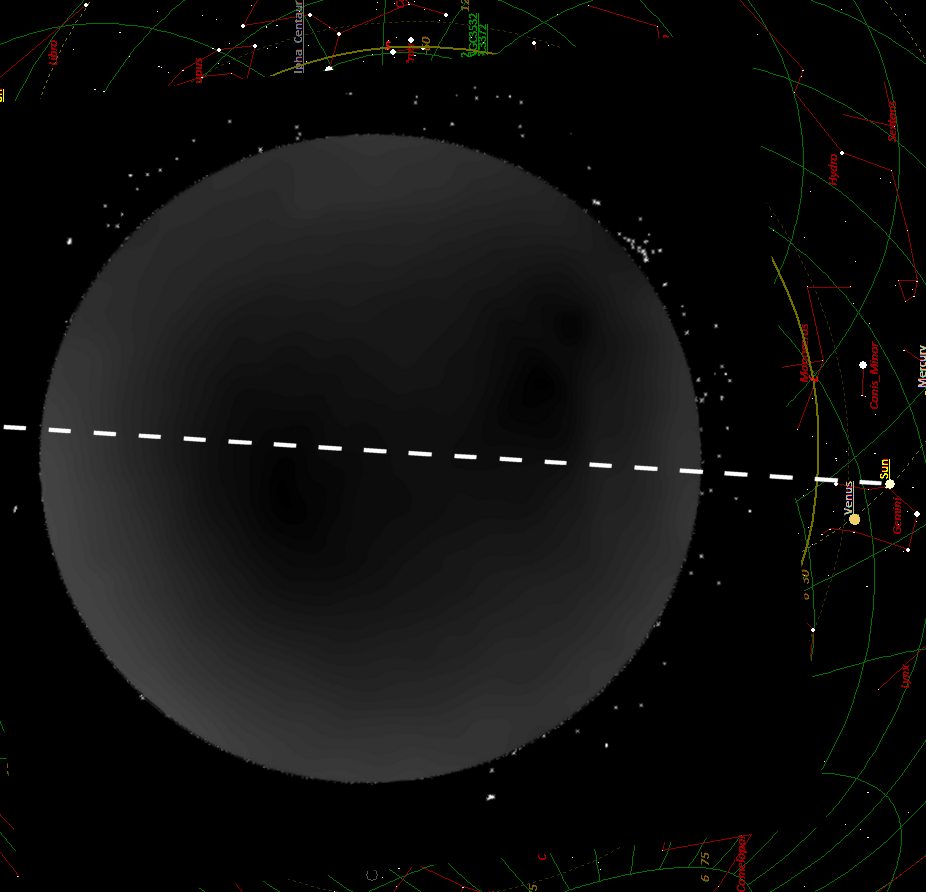
----> no influence of the position of the sun
----> no influence of the position of the Milky Way
------> Polarisation is like a ring surrounding the horizon.
Airglow is like a ring
surrounding
the horizon.
-----> Airglow is the
dominant factor for the polarization of the night sky.








































